Packungsgrößen (1)
| Code | Packungsgröße | Einzelpreis | Boxpreis pro Stück | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Produktnr. & Packungsgröße | Einzelpreis | |||

|
Code
A0805,0500
|
Packungsgröße
500 g
|
Einzelpreis
Stück
147,30€
|
Boxpreis pro Stück
|
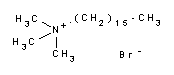
Technische Daten
- Schmelzpunkt:
- 250°C (Zers.)
- Physikalische Daten:
- fest
- Produktnummer:
- A0805
- Produktname:
- Cetyltrimethylammoniumbromid (CTAB) BioChemica
- Spezifikation:
- Gehalt (titr.): min. 99 %
Schwermetalle (als Pb): max. 0,001 %
Wasser (K.F.): max. 1 %
Fe: max. 0,001 %
- Gefahrenpiktogramme
-
- UN:
- 3077
- Klasse/PG:
- 9/III
- ADR:
- 9/III
- IMDG:
- 9/III
- IATA:
- 9/III
- WGK:
- 3
- Lagerung:
- RT
- Signalwort:
- Gefahr
- GHS Symbole:
- GHS05
GHS07
GHS09
- H-Sätze:
- H302
H315
H318
H335
H400
- P-Sätze:
- P261
P305+P351+P338
P310
P321
P330
P362+P364
P405
P501
- EINECS:
- 200-311-3
- HS:
- 29239000





