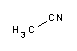Comments
About acetonitrile - Acetonitrile emission lines were detected by the radio telescope in the nucleus of comet C/1973 E1 (Kohoutek) on December 1, 1973. ESO astronomers, with the help of the ALMA telescope, first detected larger amounts of acetonitrile around the young star MWC 480 in April 2015. - Production - Production possibilities are nucleophilic substitution reactions of, for example, bromomethane with sodium cyanide (NaCN). Industrially, acetonitrile is produced in relatively small quantities as a by-product in the manufacture of acrylonitrile. Price and availability are therefore linked to the production of polyacrylonitrile. - Properties - When heated to high temperatures and in case of fire, acetonitrile gives off toxic gases such as hydrogen cyanide and nitrogen oxides. Explosive mixtures are formed with air. Acetonitrile attacks rubber and dissolves many polymers. In contact with sulfuric acid under heat, explosive polymerization may occur. Acetonitrile forms with water an azeotropic mixture of 83.7% by weight acetonitrile to 16.3% by weight water and a boiling point of 76.5 °C, 5.5 K below the boiling point of pure acetonitrile. - Safety characteristics - Acetonitrile forms highly flammable vapor-air mixtures. The compound has a flash point of 2 °C. The explosion range is between 3.0% by volume (50 g/m3) as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and 17% by volume as the upper explosion limit (UEL). The limiting concentration of oxygen is 12.7 vol% at 25 °C. The width of the limit opening was determined to be 1.5 mm. This results in an assignment to explosion group IIA. The ignition temperature is 525 °C. The substance is therefore assigned to temperature class T1. The electrical conductivity is rather low, 6108 Sm1. - Usage - Acetonitrile is a common solvent in the laboratory, in chemical analysis (e.g. HPLC) and in technical chemistry, mainly for the extraction of 1,3-butadiene. Acetonitrile is used as a solvent for conductive salts in double layer capacitors. - Acetonitrile-d3 - Fully deuterated acetonitrile (acetonitrile-d3), in which the three hydrogen atoms have been replaced by deuterium, is used as a solvent in NMR spectroscopy. - Safety information - Acetonitrile is an irritant. It is harmful by inhalation, ingestion and skin contact. Acetonitrile is absorbed through the skin (percutaneously) and acts as a blood poison in the body. Acetonitrile has low toxicity at low doses. It is metabolized to hydrogen cyanide, which is the cause of the observed symptoms. Symptoms are usually delayed (between 2 and 12 hours) because it takes time for the body to metabolize acetonitrile to cyanide. Cases of poisoning by inhalation, oral ingestion or skin absorption in humans are rare but not unknown. Symptoms that do not appear until several hours after exposure include difficulty breathing, low pulse, nausea and vomiting. In severe cases, convulsions and coma may occur, followed by death from respiratory failure. Measures to be taken are the same as for cyanide poisoning.
FAQs
What is the CAS number of Acetonitrile?
The CAS number of Acetonitrile is 75-05-8.CAS Acetonitrile?
The CAS number of Acetonitrile is 75-05-8.CAS 75-05-8?
The CAS number 75-05-8 is assigned to Acetonitrile.What is acetonitrile?
Acetonitrile is a polar organic solvent, with the formula CH3CN. It is the organic nitrile with the simplest possible structure. The nitrogen atom in the molecule contains two unpaired electrons which give it its reactivity and stability properties. It is a colorless liquid, widely used because it is miscible with water and a wide variety of organic solvents, with the exception of saturated hydrocarbons (petroleum fractions), has a low melting point and a low absorbance in the near-ultraviolet spectrum (200 nm - 400 nm). Because of this, its applications are many and varied. Acetonitrile is also known as methyl cyanide, cyanomethane or ethanonitrile. What is acetonitrile used for?
The applications of acetonitrile are many and varied: solvent for butadiene extraction; chemical intermediate for the manufacture of pesticides such as acetamipride; solvent for organic and inorganic compounds. It is also used as a raw material for the production of acetophenone, thiamine, acetamidine, etc.; for the extraction of tars, phenols and colorants in petroleum hydrocarbons (since the latter are insoluble in acetonitrile); in the production of acrylic fibers, manufacture of pharmaceuticals, nitrile rubber, ABS resins, etc. In organic synthesis it is used as an aprotic polar solvent for the preparation of drugs, intermediates, oligonucleotides and peptides. For analytical determinations, high purity acetonitrile is a widely used solvent, being especially suitable for chromatographic techniques. In recent years, the use of Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) has grown significantly. The increased speed of analysis, high efficiency, high resolution, robustness, reliability and commercial availability of a wide range of UHPLC instruments and stationary phases, with significant improvements in the technology of this equipment (detectors, automatic injectors, pumps, columns, etc.), has led to more and more laboratories acquiring UHPLC equipment and to the development of methods for the analysis of pharmaceuticals, for example, using this technique. To achieve maximum performance of these UHPLC systems, the use of suitable solvents of high purity is recommended to increase detection sensitivity, improve quantification accuracy and protect the UHPLC systems from particulate impurities that can clog and block the system. Acetonitrile is also used in liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS), e.g. for peptide and protein analysis, for spectroscopy, pesticide residue analysis, DNA synthesis, etc. What are the applications of acetonitrile?
The applications of acetonitrile are many and varied: solvent for butadiene extraction; chemical intermediate for the manufacture of pesticides such as acetamipride; solvent for organic and inorganic compounds. It is also used as a raw material for the production of acetophenone, thiamine, acetamidine, etc.; for the extraction of tars, phenols and colorants in petroleum hydrocarbons (since the latter are insoluble in acetonitrile); in the production of acrylic fibers, manufacture of pharmaceuticals, nitrile rubber, ABS resins, etc. In organic synthesis it is used as an aprotic polar solvent for the preparation of drugs, intermediates, oligonucleotides and peptides. For analytical determinations, high purity acetonitrile is a widely used solvent, being especially suitable for chromatographic techniques. In recent years, the use of Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) has grown significantly. The increased speed of analysis, high efficiency, high resolution, robustness, reliability and commercial availability of a wide range of UHPLC instruments and stationary phases, with significant improvements in the technology of this equipment (detectors, automatic injectors, pumps, columns, etc.), has led to more and more laboratories acquiring UHPLC equipment and to the development of methods for the analysis of pharmaceuticals, for example, using this technique. To achieve maximum performance of these UHPLC systems, the use of suitable solvents of high purity is recommended to increase detection sensitivity, improve quantification accuracy and protect the UHPLC systems from particulate impurities that can clog and block the system. Acetonitrile is also used in liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS), e.g. for peptide and protein analysis, for spectroscopy, pesticide residue analysis, DNA synthesis, etc. What is the melting point of acetonitrile?
The melting (freezing) point of acetonitrile is -45 °C. What is the boiling point of acetonitrile?
The boiling point of acetonitrile is 82 °C. What is the solubility of acetonitrile?
Acetonitrile is miscible with methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, ether, acetamide solutions, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, ethylene chloride and with many unsaturated hydrocarbons; immiscible with many saturated hydrocarbons (petroleum fractions). What is the density of acetonitrile?
The density of acetonitrile is 0.786 g/mL at 25 °C.What is the dipole moment of acetonitrile?
The dipole moment of acetonitrile is 3.92 D. What is the dielectric constant of acetonitrile?
The dielectric constant (permittivity) of acetonitrile is 37.5 at 20 °C. What are the safety precautions for acetonitrile?
The safety indications for acetonitrile according to the CLP (Classification, Labeling and Packaging) Regulation are: H225, H302+H312+H332, H319; P210, P280, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338, P403+P235, P501. The symbols or pictograms according to GHS (Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals) are: GHS02 and GHS07. Acetonitrile is for professional use only. The Safety Data Sheet (SDS) can be consulted by following this link https://www.itwreagents.com/download_file/sds/221881/eu/sds_221881_en.pdf. Where to buy acetonitrile?
You can purchase PanReac AppliChem brand acetonitrile from ITW Reagents through its worldwide network of distributors, or through the online store if you are a registered ITW Reagents customer. Follow this link to find a distributor in your country https://www.itwreagents.com/rest-of-world/en/distributors-rw. If you wish to purchase acetonitrile for production processes, please contact us directly.